MKV Files Explained: Common Questions & Solutions | Google Discover
Are you frustrated by the limitations of traditional video formats? The Matroska Multimedia Container (MKV) offers a revolutionary approach to storing and managing your digital media, providing unparalleled flexibility and features that empower you to create and enjoy a richer viewing experience.
In an age where digital entertainment reigns supreme, the ability to store and manage media effectively is more crucial than ever. The Matroska Multimedia Container, commonly known as MKV, emerges as a powerful solution to meet the ever-evolving demands of the multimedia landscape. Designed as an open standard, MKV transcends the limitations of its predecessors, offering a level of versatility and control previously unattainable. With its capacity to hold an unlimited number of video, audio, picture, or subtitle tracks in a single file, MKV is the preferred choice for a wide array of uses, from preserving the integrity of your favorite films to creating immersive viewing experiences.
At its core, MKV is a container format, a digital vessel designed to hold various multimedia elements. Unlike codecs, which are responsible for encoding and decoding the actual video and audio data, MKV provides the framework for organizing and presenting these elements in a cohesive package. Think of it as a meticulously crafted digital box that can accommodate a multitude of digital treasures, making it a versatile tool for video projects of all scopes. Unlike older formats like AVI or MP4, MKV's open standard allows for greater flexibility, making it a prime choice for the next generation of media.
The Matroska project, the driving force behind the MKV container, was conceptualized with the goal of creating a format that could evolve with the ever-changing needs of the multimedia world. This endeavor started as a fork of the MCF project but differentiated itself through the use of EBML (Extensible Binary Meta Language), a binary derivative of XML. This approach allowed for a more robust and scalable format, capable of accommodating the diverse and dynamic nature of digital media.
The MKV format supports a vast array of features, including multiple audio and subtitle tracks within a single file. This capability is particularly useful for films and TV shows with multiple languages or alternative audio commentaries. You could have one audio track for the English language version and another for the director's commentary, all within the same MKV file. This versatility, coupled with the ability to contain different individual file formats within it, makes MKV an essential part of any video project.
Beyond its storage capabilities, MKV also boasts support for various video and audio compression formats. This allows for optimal compression, ensuring a balance between file size and image quality. Furthermore, the MKV format allows for the integration of metadata, such as chapter markers and descriptive information, enhancing the user's experience. For example, when a chapter marker is included in a video, the viewer can jump to specific scenes in the movie quickly.
The benefits of using MKV are not limited to professional video editors or home theater enthusiasts. MKV is an open-source format and can be used for free. With its versatility, adaptability, and open-source design, it's a practical solution for anyone who wants to effectively and efficiently organize, store, and share their digital media.
Here are some of the key characteristics of MKV, outlining what sets it apart:
- Open Standard: As an open standard, MKV is freely available for anyone to use, and its specifications are publicly accessible.
- Versatile Container: MKV can contain a broad array of multimedia elements, including video, audio, pictures, and subtitles, all within a single file.
- Multiple Tracks: It supports an unlimited number of audio, video, and subtitle tracks, offering flexibility for multilingual content or alternate audio options.
- Metadata Support: MKV includes robust metadata capabilities, enabling the inclusion of chapter markers, descriptive information, and more, thereby enhancing the user experience.
- Compression Compatibility: MKV can accommodate various video and audio compression formats, making it a good choice for high-quality media.
- Container, Not a Codec: Unlike codecs, MKV is a container format, which means it holds the audio and video, not compresses them.
A few players support the MKV file format natively. These are some of the most popular ones:
- VLC Media Player: VLC is a free, open-source media player available on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It has native support for MKV files.
- MPV Player: MPV is a free, open-source media player that supports a wide range of media formats.
- PotPlayer: PotPlayer is a free multimedia player that supports MKV files on Windows.
- Kodi: Kodi is a free, open-source media player software for video and audio.
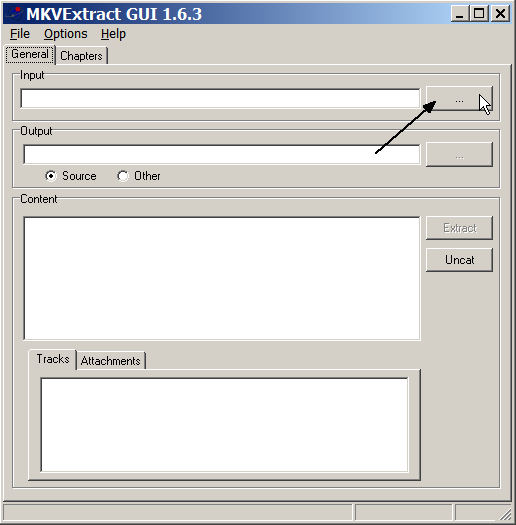
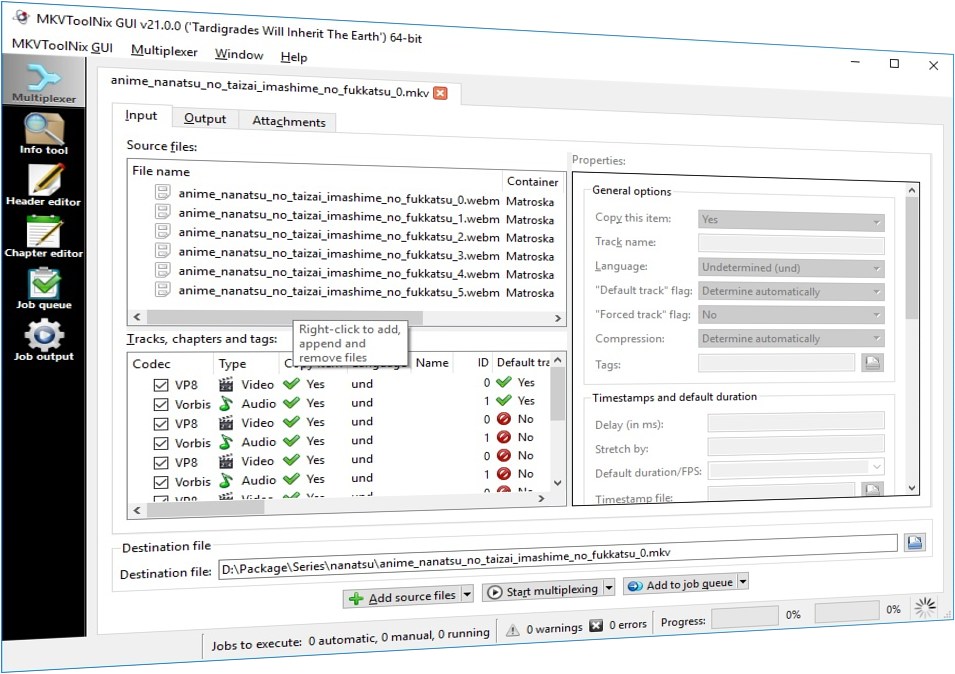
Tools such as MKVToolNix are used to create, alter, and inspect Matroska and WebM files on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. These tools empower users to fully manage and interact with MKV files, facilitating everything from basic file manipulation to advanced editing and customization. The MKVToolNix suite's main component is MKVMerge, which allows users to create MKV files from other formats. This capability is important, as it helps users gather various video files, audio files, and subtitle files into one single container.
If you are encountering problems with the Docker image, please report a bug in the relevant GitHub repository. For any problems such as file permissions and problems with differing user IDs inside and outside the container, please review the documentation provided for specific instructions on how to run the image and solve these issues.
The Media Foundation supports MKV container features in the following ways:
- If one or more video tracks are present, the first track will be played.
- If one or more audio tracks are present, the first track will be played.
- Caption tracks are supported, but are not selected (played) by default.
In conclusion, MKV is more than just a file format; it's a commitment to media quality, flexibility, and open standards. It allows for greater control over how your content is packaged, stored, and shared. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, MKV is well-positioned to remain a top choice for storing and managing video.